






|
Ancient Rome:
In historiography, ancient Rome is Roman
civilization from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th
century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the
5th century AD, encompassing the Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic
and Roman Empire until the fall of the western empire. The
civilization began as an Italic settlement in the Italian
peninsula, dating from the 8th century BC, that grew into the
city of Rome and which subsequently gave its name to the empire
over which it ruled and to the widespread civilisation the
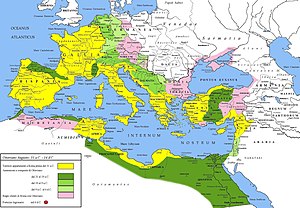
empire developed. The Roman empire expanded to become one of the
largest empires in the ancient world, though still ruled from
the city, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants
(roughly 20% of the world's population) and covering 5.0 million
square kilometres at its height in AD 117.
In its many centuries of existence, the Roman state evolved from
a monarchy to a Classical Republic and then to an increasingly
autocratic empire. Through conquest and assimilation, it
eventually dominated the Mediterranean region, Western Europe,
Asia Minor, North Africa, and parts of Northern and Eastern
Europe. It is often grouped into classical antiquity together
with ancient Greece, and their similar cultures and societies
are known as the Greco-Roman world.
Ancient Roman civilisation has contributed to modern language,
religion, society, technology, law, politics, government,
warfare, art, literature, architecture and engineering. Rome
professionalised and expanded its military and created a system
of government called res publica, the inspiration for modern
republics such as the United States and France. It achieved
impressive technological and architectural feats, such as the
construction of an extensive system of aqueducts and roads, as
well as the construction of large monuments, palaces, and public
facilities.
By the end of the Republic (27 BC), Rome had conquered the lands
around the Mediterranean and beyond: its domain extended from
the Atlantic to Arabia and from the mouth of the Rhine to North
Africa. The Roman Empire emerged with the end of the Republic
and the dictatorship of Augustus Caesar. 721 years of
Roman-Persian Wars started in 92 BC with their first war against
Parthia. It would become the longest conflict in human history,
and have major lasting effects and consequences for both
empires. Under Trajan, the Empire reached its territorial peak.
Republican mores and traditions started to decline during the
imperial period, with civil wars becoming a prelude common to
the rise of a new emperor. Splinter states, such as the
Palmyrene Empire, would temporarily divide the Empire during the
crisis of the 3rd century.
Plagued by internal instability and attacked by various
migrating peoples, the western part of the empire broke up into
independent "barbarian" kingdoms in the 5th century. This
splintering is a landmark historians use to divide the ancient
period of universal history from the pre-medieval "Dark Ages" of
Europe. The eastern part of the empire endured through the 5th
century and remained a power throughout the "Dark Ages" and
medieval times until its fall in 1453 AD. Although the citizens
of the empire made no distinction, the empire is most commonly
referred to as the "Byzantine Empire" by modern historians
during the Middle Ages to differentiate between the state of
antiquity and the nation it grew into.
According to the founding myth of Rome, the city was founded on
21 April 753 BC by the twin brothers Romulus and Remus, who
descended from the Trojan prince Aeneas, and who were grandsons
of the Latin King Numitor of Alba Longa. King Numitor was
deposed by his brother, Amulius, while Numitor's daughter, Rhea
Silvia, gave birth to the twins. Since Rhea Silvia had been
raped and impregnated by Mars, the Roman god of war, the twins
were considered half-divine.
According to legend, Romulus and Remus, were raised by a
she-wolf. The new king, Amulius, feared Romulus and Remus would
take back the throne, so he ordered them to be drowned. A
she-wolf (or a shepherd's wife in some accounts) saved and
raised them, and when they were old enough, they returned the
throne of Alba Longa to Numitor.
The twins then founded their own city, but Romulus killed Remus
in a quarrel over the location of the Roman Kingdom, though some
sources state the quarrel was about who was going to rule or
give his name to the city. Romulus became the source of the
city's name. In order to attract people to the city, Rome became
a sanctuary for the indigent, exiled, and unwanted. This caused
a problem, in that Rome came to have a large male population but
was bereft of women. Romulus visited neighboring towns and
tribes and attempted to secure marriage rights, but as Rome was
so full of undesirables he was refused. Legend says that the
Latins invited the Sabines to a festival and stole their
unmarried maidens, leading to the integration of the Latins with
the Sabines.
Another legend, recorded by Greek historian Dionysius of
Halicarnassus, says that Prince Aeneas led a group of Trojans on
a sea voyage to found a new Troy, since the original was
destroyed at the end of the Trojan War. After a long time in
rough seas, they landed on the banks of the Tiber River. Not
long after they landed, the men wanted to take to the sea again,
but the women who were traveling with them did not want to
leave. One woman, named Roma, suggested that the women burn the
ships out at sea to prevent their leaving. At first, the men
were angry with Roma, but they soon realized that they were in
the ideal place to settle. They named the settlement after the
woman who torched their ships.
The Romans gradually subdued the other peoples on the Italian
peninsula, including the Etruscans. The last threat to Roman
hegemony in Italy came when Tarentum, a major Greek colony,
enlisted the aid of Pyrrhus of Epirus in 281 BC, but this effort
failed as well. The Romans secured their conquests by founding
Roman colonies in strategic areas, thereby establishing stable
control over the region of Italy they had conquered. |